

Incorporating game elements into English for Academic Purposes (EAP) teaching has proven effective in enhancing student engagement and learning. However, formulating such activities can be time-consuming and challenging for educators. This essay examines the use of XIPU AI in developing interactive and engaging EAP exercises, sharing insights from various implementations across content creation, ideas generation, instructions and titles formulation, and activity refinement. Despite the valuable assistance provided by AI, its limitations require careful consideration. By leveraging AI's capabilities alongside pedagogical expertise, EAP classrooms can foster greater student engagement and enjoyment.
Keywords: EAP teaching, XIPU AI, Gamified Activities, Student Engagement
Encouraging positive affect and student engagement is crucial in establishing a conducive learning environment and motivating students to undertake future learning tasks (Sabourin and Lester, 2014). Incorporating game elements into teaching, as evidenced by its positive impact on enhancing knowledge and exam performance, has proven to be an effective method for increasing student engagement and motivation(Dichev and Dicheva, 2017; Orhan Göksün and Gürsoy, 2019). Within EAP teaching, gamified and interactive class activities have been widely adopted as a strategy to enhance student engagement and learning. However, the design of these activities can be both challenging and time-intensive. This semester, I have employed XIPU AI to develop more dynamic and interactive teaching activities for EAP classes. Drawing from personal experiences, I would like to share the various ways XIPU AI can be harnessed to make learning more engaging and enjoyable.
One of the most compelling applications of XIPU AI in designing EAP classroom activities lies in its capacity to produce the necessary materials quickly. Consider the challenge of creating an ‘Essay Puzzle Challenge’ to deepen students' comprehension of coherence and cohesion in academic writing. Typically, the most demanding aspect is locating an essay that exemplifies strong cohesion and a clear organizational structure. However, XIPU AI can streamline this process significantly by generating an essay with these characteristics. While I still need to customize the essays by adjusting language complexity, length and emphasizing specific aspects of cohesion and structure to align with instructional objectives, the help of XIPU AI has greatly minimized the time and effort expended.
The content generation capabilities of XIPU AI have been instrumental in the creation of various instructional activities. Beyond generating sample essays, XIPU AI can produce topic-relevant questions that enrich a wide spectrum of activities, ranging from board games and mingling activities to practice sessions for speaking assessments. Additionally, XIPU AI can also be employed to craft role description cards which are integral components of role-play activities. Such activities, mirroring real-life scenarios, not only enhance student retention, understanding, and engagement with the course material but also facilitate collaborative learning and cultivate critical thinking skills (Piscitelli, 2020; Stevens, 2015). Nonetheless, role-play activities can pose challenges as students often require support in understanding and internalizing the characteristics and viewpoints of their assigned roles. In this context, XIPU AI proves invaluable by crafting comprehensive role descriptions. The screenshot below captures the interaction between XIPU AI and me as we collaborated to generate role description cards for a role-play activity focused on corporate social responsibility (CSR). The AI-generated role descriptions facilitated students in understanding their roles, thereby enhancing their participation in more meaningful discussions.
XIPU AI also emerges as a powerful brainstorming partner, offering valuable suggestions for engaging activities based on specific materials or topics. For example, in one of my lessons, I sought a warm-up activity to introduce students to diverse strategies for attracting investment to startups. Upon inputting my requirements into XIPU AI, it proposed an activity called ‘Investment Runway.’
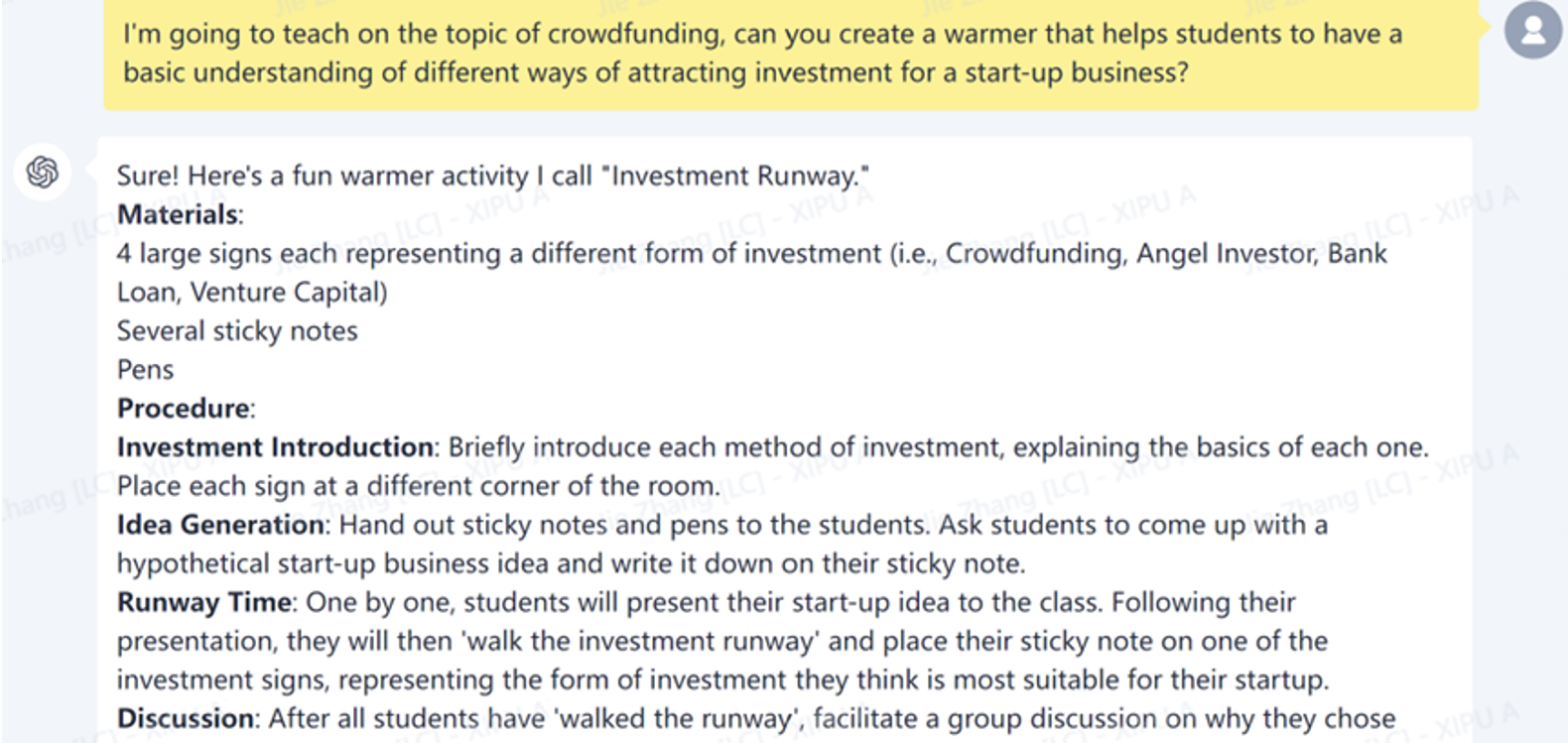
While the concept was appealing, the suggested activity proved overly extensive given our time constraints and the lesson's learning objectives. To address this, I revised my prompt to request shorter activities, which led to a list of more time-efficient warm-up exercises.
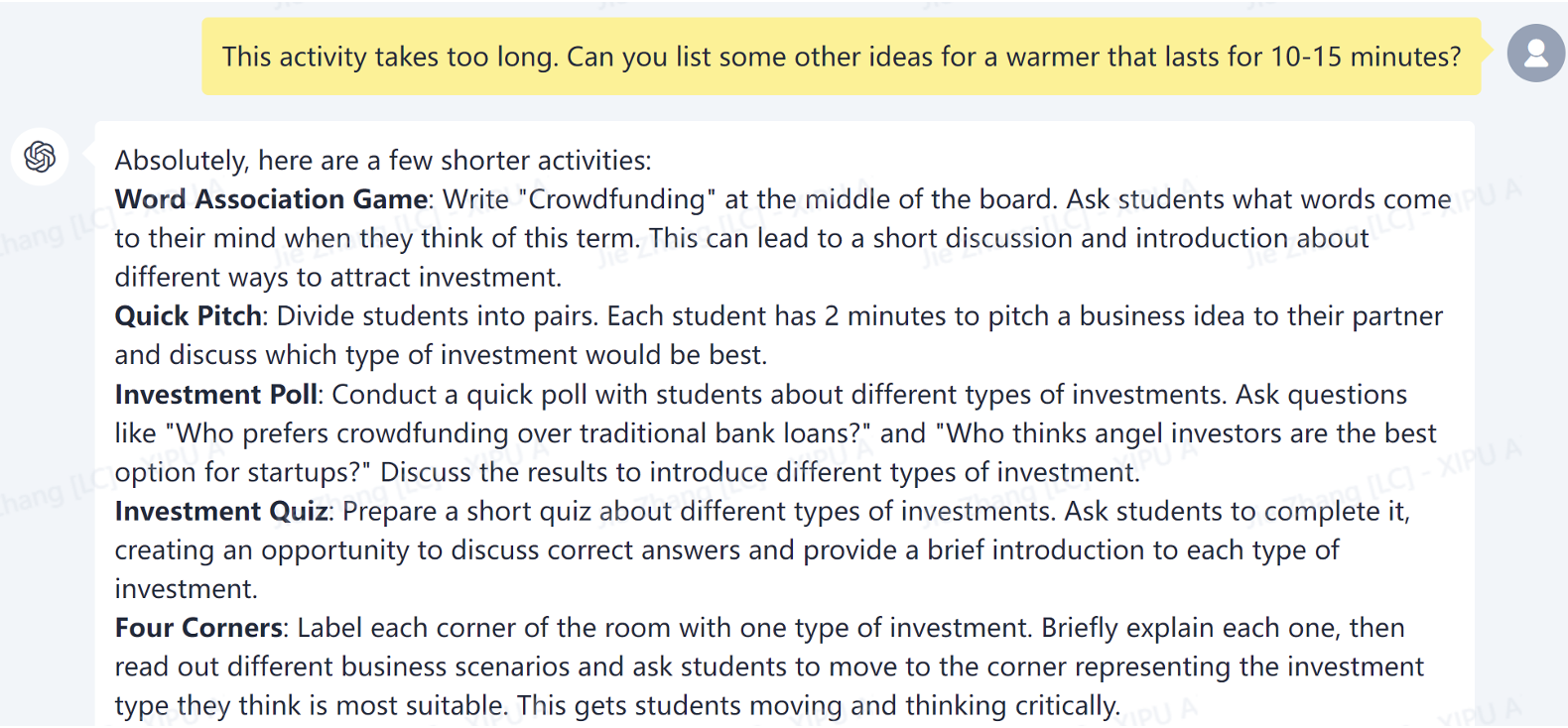
Drawing inspiration from these suggestions, I adapted the 'Investment Runway' idea into a simpler format and incorporated the concept of another AI-generated idea, the 'investment poll.' While I did not directly implement the AI-generated ideas, they play a crucial role in the brainstorming process and are invaluable in expanding my thinking and sparking creativity.
In addition to content creation and idea generation, XIPU AI can also aid in crafting clear instructions for activities. The screenshot below illustrates instructions generated by XIPU AI for a vocabulary Bingo game. However, these instructions may occasionally be overly detailed and lack relevance, requiring further refinement and precise prompts to enhance clarity and conciseness.

Another interesting aspect I have noticed while exploring the use of XIPU AI in designing classroom activities is its ability to craft engaging and catchy names, which is crucial for sparking students' interest and curiosity during activity introductions. For example, compare the straightforward 'matching words with their definitions' to the captivating 'Vocabulary Puzzle Race,' or 'exploring the module by answering questions' to the enticing 'Module Scavenger Hunt.' The two latter more effectively captivate students relatively. However, it is important to acknowledge that AI does not consistently deliver perfect suggestions. Sometimes, it may generate more generic names or demonstrate a lack of contextual understanding.
After an activity is designed, obtaining feedback and suggestions for improvement is not always easy. In this regard, XIPU AI can offer valuable insights by refining language, checking instruction clarity, analyzing content, and assessing the potential engagement level of the activity. This feedback can be instrumental in assisting teachers refine their designs and ensuring that they are both educationally sound and engaging for students. Again, it is crucial for teachers to critically evaluate the feedback provided by AI and tailor their prompts to ensure the AI understands their requirements clearly.
In conclusion, the integration of XIPU AI into the design of EAP classroom activities holds significant promise for enhancing teaching and learning experiences. XIPU AI has proven instrumental in reducing preparation time and stimulating creativity by efficiently generating tailored content materials and providing activity suggestions. Notably, the AI’s capabilities extend beyond mere content and idea generation to encompass crafting clear instructions, engaging titles, and refining the designed activities from various perspectives. The activities facilitated by XIPU AI have been warmly received by my students, demonstrating a clear boost in their engagement and participation.
While the assistance of XIPU AI offers notable advantages, direct application of AI-generated content may not always be feasible. It is essential for educators to critically evaluate and adapt AI-generated outputs to closely align with specific learning objectives and classroom contexts. Furthermore, the content generated by AI relies on the specific prompts provided. This means that without precise instructions regarding context, such as student numbers, language level, or desired learning outcomes, AI may not produce optimally relevant or engaging content. Ultimately, when used thoughtfully, XIPU AI acts as a powerful tool for adding more excitement to EAP teaching, enriching both the educational process and the overall student experience.
Dichev, C., and Dicheva, D. (2017). ‘Gamifying education: What is known, what is believed and what remains uncertain: A critical review’, International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 14(1), pp. 9. doi:10.1186/s41239-017-0042-5
Piscitelli, A. (2020) ‘Effective Classroom Techniques for Engaging Students in Role-Playing’, Teaching Innovation Projects, 9(1), pp. 1–8. doi:10.5206/tips.v9i1.10320.
Orhan Goksun, D. and Gursoy, G. (2019). ‘Comparing success and engagement in gamified learning experiences via Kahoot and Quizizz’, Computers & Education, 135, pp.15–29.doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2019.02.015
Sabourin, J.L. and Lester, J.C. (2014) ‘Affect and engagement in game-based learning environments’, IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 5(1), pp. 45-56–56. doi:10.1109/T-AFFC.2013.27.
Stevens, R. (2015) ‘Role-play and student engagement: reflections from the classroom’, Teaching in Higher Education, 20(5), pp. 481–492. doi:10.1080/13562517.2015.1020778.